What is IBD?
Inflammatory bowel disease, also referred to as IBD, is a term used to describe two conditions, ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. Both ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease are long term conditions with no known cure.
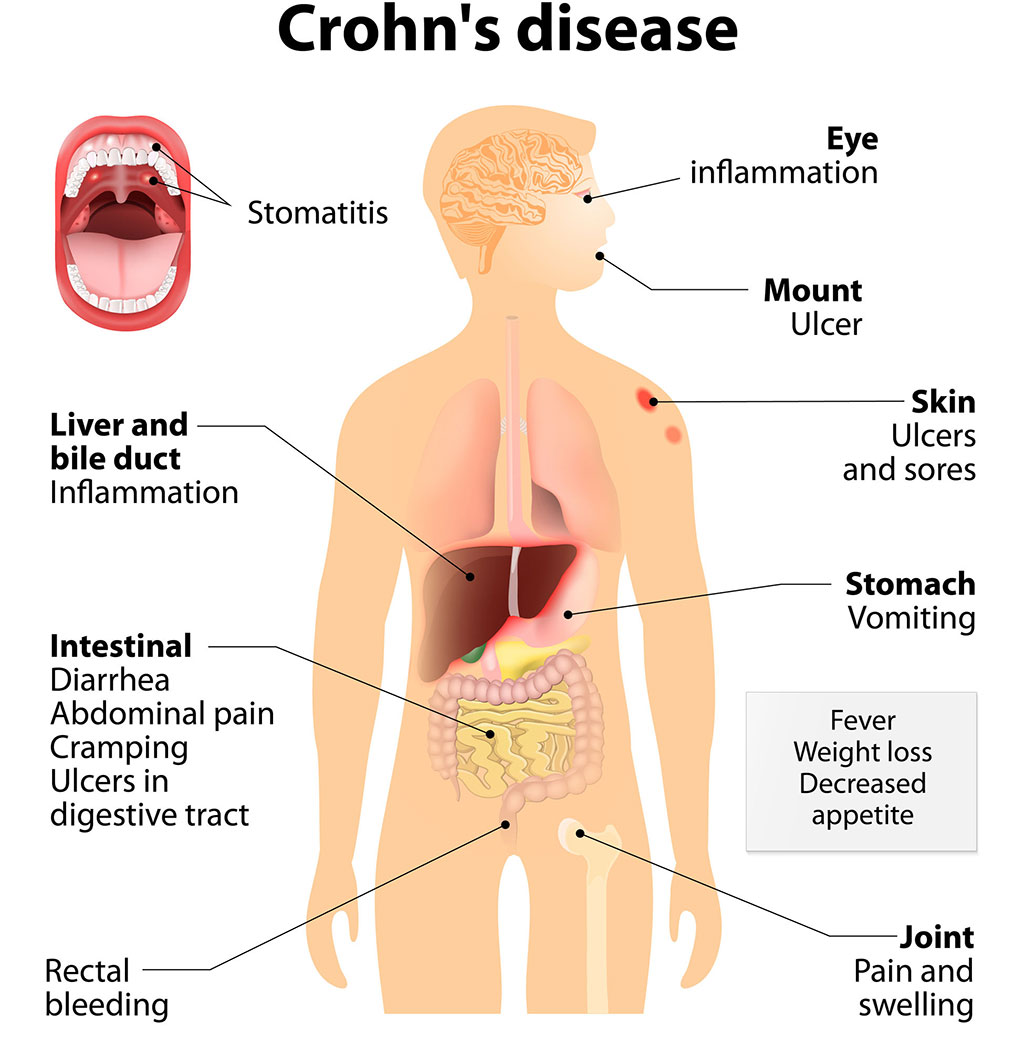
Crohn’s disease is a chronic disease that causes inflammation anywhere in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. This disease causes canker-like sores, abscesses and strictures. Crohn’s can cause other parts of the body to become inflamed, such as joints, mouth, eyes and skin. In children, Crohn’s may cause a decrease in growth and a delay in puberty.
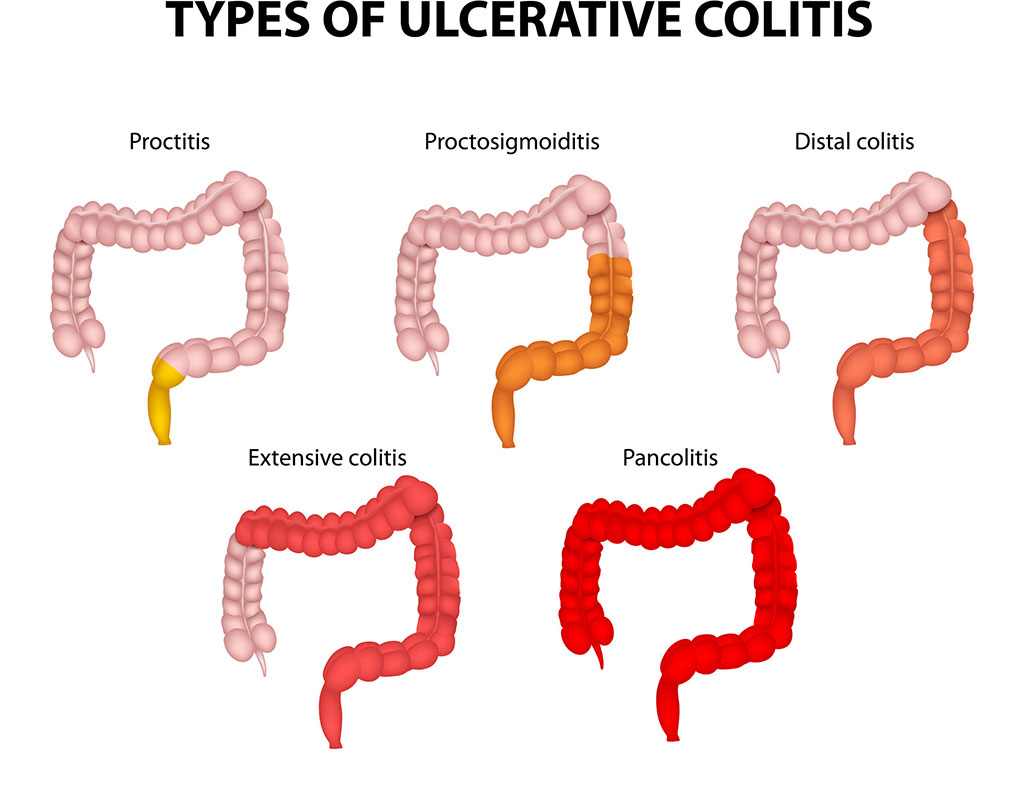
Ulcerative colitis is a chronic disease that causes inflammation in the innermost lining of the large intestine (colon).
Crohn’s disease symptoms can include:
- Chronic diarrhea
- Blood or mucus in stools
- Weight loss
- Abdominal pain
- Fatigue
- Lack of appetite
- Malnutrition
- Abscesses
- Canker-like sores
Ulcerative colitis symptoms can include:
- Chronic diarrhea
- Blood or mucus in stools
- Weight loss
- Abdominal pain
- Fatigue
- Lack of appetite
- Malnutrition
- Abscesses
- Canker-like sores
Is inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) the same thing?
No. Although the conditions sound similar, the two are VERY different.
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a disorder affecting the intestine. IBS involves problems with motility (how digested food moves through the intestines) and sensitivity (how the brain interprets signals from the intestinal nerves), leading to abdominal pain, changes in bowel patterns and other symptoms. Although often disruptive, debilitating and embarrassing, it is not life threatening, nor does it lead to cancer or other more serious illnesses.
*Crohns and Colitis Foundation of America, www.crohnscolitisfoundation.org
*Canadian Digestive Health Foundation, www.cdhf.ca
